What is HDR TV?
High Dynamic Range (HDR) presents images and videos with more luminance and contrast and with brighter colors. Most TVs today have HDR features to enable improvement and appeal.
HDR (High Dynamic Range) is an extended dynamic range and a general name for the technology. Previously, 8-bit SDR video was used, but with the advent of OLED panels, screens have learned to transmit much more shades, so it became necessary to create a 10-bit video technology. That’s how the dynamic range came about.
HDR is available in four formats, namely HDR10, HDR10+, Dolby Vision, and HLG.
HDR TV meaning — this refers to the high dynamic range of the video image on the TV screen.
The dynamic range of an image indicates the difference in brightness between the lightest point in the picture and the darkest point.
The human eye is better able to perceive greater differences in brightness than television equipment can convey. Therefore, to bring the image on the screen closer to the original, it was necessary to use a technology like HDR.
Technical Features of HDR
The task of the extended dynamic range is to increase the detail in the video. Details of the picture disappear in the dark or light areas of the image. For example, the sun is bright in the frame, and as a result, nothing is visible until the brightness decreases. But with HDR, there will be visible details in the bright area, such as sunlight and clouds.
Not all HDR TVs are created equally — find out why.
Some people might think that if all TVs have HDR, they’re created equal, but that’s not true. A test involving some consumers and justified by the manufacturers agreed that not every HDR TV can produce equally rich and amazing lifelike images. This happens because of specific technologies designed within a particular TV.
HDR technology enhances the naturalness and realism of video.
SDR (Standard Dynamic Range) — Standard Dynamic Range brightness works for regular TV and video. It’s what we are used to.
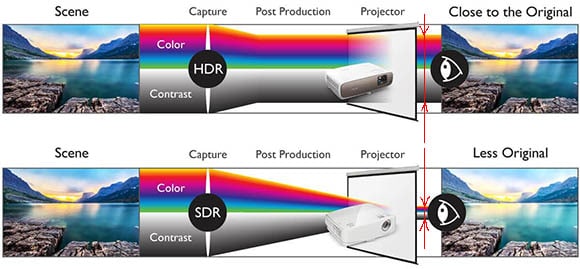
Note the amount of information in the video stream (picture above) at SDR quality and HDR. This video stream is indicated by the red line.
HDR is bright whites and deep blacks, and even more detail within those areas.
It’s impossible to show what this looks like if your monitor doesn’t support HDR, but consider the simulated photo below (from Dolby). Extended range on the right.

Imagine seeing bright reflections of sunlight on metal surfaces or flowers in a field with a coloring that a normal TV would not reflect.
Increase dynamic range by increasing brightness and increasing the number of gradations of each color. That’s why HDR video plays back on screens with a maximum brightness of at least 1000 nits, and the color gamut of such screens is increased to Rec 2020.
And it’s not just about increasing brightness, it’s about increasing the dynamic range to reflect more gradations of color, so we see more detail in the bright area of the screen or the dark area.
And the screen matrix itself has 10 bits per color channel, producing 1024 shades per subpixel. That’s almost a billion shades of color per pixel. These are all characteristics of advanced and expensive televisions.
Conventional SDR matrices have 8 bits and 16 million shades.
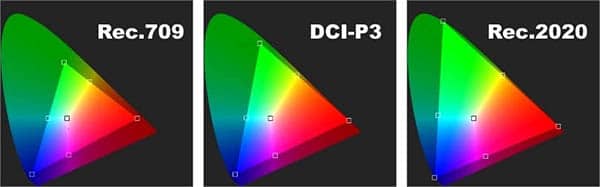
Rec.709 color gamut is used for HD contenthe development for the field of Ultra HD production and sales is Rec.2020.
To understand just how big of a leap this is, it’s worth mentioning that Rec.709 covers about 36% of color visible to the human eye, while Rec.2020 covers about 75%.
For LED TVs with a liquid crystal matrix, matrix backlighting accuracy is very important for proper extended-range operation. And local dimming allows the display to increase brightness and contrast, which is necessary for HDR. You need Full Array backlighting with more dimming zones.
A simple TV is unable to display small differences in brightness. Halftones merge into a single bright spot (in the case of a bright area of the image).
As the dynamic range increases, the peak brightness becomes greater. The color space, the number of colors and tones increase, and details on the bright or dark part of the image become distinguishable.
Well-implemented HDR has a greater impact on image quality than going from Full HD to 4K.
Values for Luminance, Black Level
One nit is equivalent to the light produced by a single candle, and a nit is a unit of the measure of brightness and is equals one candela per square meter (cd/m²).
In theory, an HDR TV can deliver up to 5,000 nits. A standard TV delivers about 100-300 nits of brightness.
For HDR, the main parameters are at least 1000 nits of peak brightness and a black level of fewer than 0.05 nits. This is for LCD TVs.
For OLED screens, which have a low average brightness and much lower black levels than LCDs, the peak brightness is from 600 nits, and the black level is less than 0.0005 nits.
What Does HDR Mean in Video and Photo
Unlike HDR in photography, video is shot in HDR immediately if you want to increase the dynamic range.
When you take a photo, you take a series of photos of different light levels (different exposures) and combine them into an HDR photo. When shooting video, there is no signal processing. The image is rendered in a natural way.
What HDR has in common with photos and videos is the goal of displaying different tones to bring the image closer to reality.
The human eye has a huge dynamic range and can capture high brightness values and still distinguish details. All television technology is just trying to get closer in performance to human vision, and the end of the road is still a long way off.
Fake HDR
What is being done to fake HDR?
In an attempt to improve the picture, content creators artificially increase chromaticity and contrast. Colors look lush, and the picture itself is contrasted, but details in bright and dark scenes are lost.
In this case, turning on HDR on the TV can be detrimental to the image quality on the screen.
This is also what TV manufacturers do when regular SDR video increases brightness and contrast after analyzing the picture. Here the colors get richer, but it’s a far cry from the enhanced range that the detail of the video suffers.
HDR Formats
HDR video means transmitting and reproducing pixels with more information about the color and brightness of each pixel. This information is stored in metadata. There are dynamic and static metadata.
Video metadata is additional data that is embedded in the video stream. This information can be anything from the file name to technical data. For example, the date or geographical information about where the file was created.
Static metadata in HDR video stores information about the entire movie and does not change over time. Such data can be brightness, contrast, etc.
Dynamic metadata provides information about brightness, contrast, color, and everything else for each scene in the movie or for each frame. This is much better than static data.
There are currently four varieties of HDR: HDR10, HDR10+, HLG, and Dolby Vision.
When buying a TV, it is necessary to focus on the name of the standard itself, as all other names (HDR Effect, Quantum HDR, and so on) will be no more than a marketing ploy.

HDR10
It’s widely used because any HDR TV can support HDR10. It is the de facto HDR standard since it is open source. This implies that manufacturers are at liberty to implement it on their TVs without necessarily paying a fee.
Apart from that, note that it has several official backings from major industry-standard bodies such as the UHD Alliance. It is an open standard adopted by numerous manufacturers, streaming services from Amazon, Netflix, Apple, Disney+, and the Blu-ray Disc Association (BDA).
With this version, be assured of improved image quality. Compared to other versions, it’s not as sophisticated as they are.
According to the Consumer Electronics Association (CEA), HDR10 must meet certain standards, including 4:2:0 color subsampling, 10-bit depth and the Rec.2020 color space.
HDR10 is the original and currently the most common form of HDR. It is an open standard that has been adopted by:
- Numerous manufacturers
- Amazon, Netflix, Apple and Disney+ streaming services
- Blu-ray Disc Association (BDA)
HDR10:
- Is supported by all
- Has better picture quality than SDR but not as good as HDR10+ or Dolby Vision
- Uses static metadata

HDR10+
This is an improved version of HDR10. It supports dynamic metadata, although it is limited to 10 bits of colors.
HDR10+ is designed as an enhanced format, so devices that cannot interpret this signal simply see the HDR10 stream they can decode.
HDR10+ can be supported through HDMI 2.0b, HDMI 2.1 is not a requirement.
The catch is that it is a Samsung format. Despite the promise of no licensing fees (so anyone can use it for free), this is something of a stumbling block. It’s hard to imagine a world in which LG willingly supports a new format supported by Samsung. Other broadcasters are probably hesitant to maintenance it for the same reason.
Companies such as Amazon, Panasonic, Hisense, and Philips use HDR10+ for streaming on their devices. Currently, the manufacturers have supported 4K UHD Blu-ray on HDR10+.

What is HDR10+ Adaptive?
HDR10+ Adaptive is a TV technology that is used in many high quality televisions.
It is a way to calibrate picture settings for HDR10+ content based on the intensity of light in the room around the TV screen.
Additional Information:
- How does CEC work
- Why do you need HDMI?
- Samsung TV Dead Pixel
- IPS vs VA contrast
- Theatre Power Manager
Dolby Vision
Dolby Vision HDR is a copyrighted option from Dolby and requires a license to use.
This is the best format in comparison to the two mentioned above. Dolby Vision’s potential in displaying vibrant and beautiful calculates images on a scene basis and is dynamic. It’s among the newest format after HDR10+, and it’s ideal for home entertainment as it provides a better solution.
It is added scene-by-scene to enable it to provide better viewing of the images. The bright is better with darker blacks to enable the TV to display a full range of colors in the Rec.2020 standard. The Dolby feature will blow you away.
Dolby Laboratories Inc. was founded in 1965 and today holds one of the leading positions in sound processing, recording, and sound reproduction. You may have heard of Dolby Stereo, Dolby Surround, and Dolby Atmos. These technologies are used in both home audio equipment and cinemas, creating the most spacious and realistic sound possible with support for up to 64 speakers.
Dolby specialists began to try their hand at video content delivery algorithms. Thus Dolby 3D and Dolby Vision technologies appeared.
In simple terms, Dolby Vision is a proprietary color correction technology. To make the picture more realistic, colorists and editors in the film studio make changes in color, brightness, and contrast. All of these adjustments are recorded as auxiliary information – metadata. When you play a video, the TV can read this metadata, adjusting the screen for the best effect.
Dolby Vision content is 4K (UHD) video plus dynamic metadata. Typically, two video streams are used – one in 4K resolution and the other in HD with local brightness and additional color information for each frame.
Dolby Vision is Dolby’s proprietary HDR content format designed to enhance picture quality.
Dolby Vision has made a big push for HDR. Like HDR10+, it can have dynamic metadata. Streaming services like Netflix, Amazon, Vudu, and Apple iTunes support it, and you can find it on Blu-ray Ultra HD discs.
The development of HDR was a joint development of Samsung and Panasonic – HDR10+. The main innovation is the introduction of dynamic metadata. Thanks to this, HDR10+ format became almost equally competitive with Dolby Vision, even despite the loss in color depth.
Visually, it is difficult to determine the difference between the two formats. In any case, the quality of the picture will only be a subjective opinion.
Companies have to pay Dolby to use this technology. Dolby, on the other hand, will help make sure their televisions improve the picture. So this is an easy way for some companies to improve the video quality on their TVs.
Dolby Vision can be 12-bit or 10-bit, depending on the medium being distributed. Dynamic metadata means that HDR parameters can change from scene to scene rather than being fixed for the entire object.
What is Dolby Vision IQ?
The principle behind Dolby Vision IQ is the use of dynamic metadata encoded in Dolby Vision content. Combined with the built-in light sensor in the TV, using the encoded information to change picture settings, the picture in the frame is adjusted to provide a more accurate image.

HLG HDR Meaning
It’s a Hybrid Log-Gamma, a dynamic range imagery standard. The main reason why it was designed is for use by broadcast TVs.
The broadcasters can massively transmit signals with a wide dynamic range in support of SDR televisions and HDR televisions, hence minimizing the complexity and cost of the broadcast signal transmission.
It is royalty-free and doesn’t use metadata to display the HDR content as the other HDRs do.
If, in any case, you are planning on watching broadcast TV on your new device, then HLG will be ideal if supported. Many users are adopting podcast TVs; an example of these broadcasters is Sky UK.
On the other hand, streaming content sees the potential in HLG, and that’s why they are now taking advantage of it.
BBC Planet II can stream series and movies using its iPlayer app and HLG HDR. Sony TVM, LG, Samsung, and Panasonic both support HLG.
If you’re considering buying a new TV for use, then this can be the best to go for.

Things to consider when buying an HDR TV
The market has a wide range of TVs. If you’re looking for an HDR TV, ensure that it has HDR formats like the ones discussed above in the article.
- The mid-range should be between 600 nits for peak brightness and 450 nits for sustained brightness, support the local dimming zones and wide gamut and offer support for HDR10, HDR10+ OR Dolby Vision, HLG.
- TVs with high-end HDR must have about 1000 nits or even higher for peak brightness, and sustainable brightness is about 600 nits. Thirty-two local dimming zones will be preferable as well.
- TVs with a lower range will need about 400 nits for peak brightness and 350 nits for sustainable brightness. They must be in a position to support HDR10 and HLG.
Is HDR worthy?
If you plan to buy an expensive new TV set, then HDR cab is worth your money. Go for an HDR TV that is featured with Ultra HD Premium Certification. It will give you a true HDR viewing experience. This will entail a 4K resolution, 1000 nit peak brightness, 10-bit color depth, and a 20000:1 contrast ratio.
Images displayed by HDR are much brighter and appealing to watch. The wide color gamut is another important feature of HDR TVs.
HDR is worth it as they are gaining more popularity of late; they are now available on-stream services like Xbox games and PlayStation, among others.
Bottom line
This is a high time people jump into 4K models supported by HDR, if you haven’t bought your TV device, consider buying this set.
The above article shows that with an HDR screen, you are in a position to have an ultimate viewing experience because of the high-quality images and maximum light adjusted to favor your viewing.
Find a brand that fits your budget among LG, Sony, Hisense, Samsung, and other well-known brands.
Facebook Twitter LinkedIn Telegram Pinterest
